Introduction to biochemistry, common sense needed
Biochemistry is a field that explains whether the order of life is broken or maintained in a molecular oligopoly, and is an area that describes the energy aspects, life maintenance, and genetics in the process of energy acquisition.


In the periodic table, the most abundant molecules in life are H, C, N, and O,
Next, Na, Mg, P, S, Cl, K, and Ca are the next most abundant.
In addition, B, F, Al, Si, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, As, Se, Br, Mo, Cd, I, W can be considered to play a negative role.
Amine, Alcohol, Thiol, Ether, Aledhyde, Ketone, Carboxylic acid (Carboxylate), Ester, Amide, Imine, Phosphoric acid, Diphosphoric acid should be memorized.
It may be very difficult, but it is essential because it is used for common sense.
wps.prenhall.com/wps/media/objects/3085/3159329/blb2504.html
I think you can refer to it here.
To talk about biomolecules, which are mainly mentioned in biochemistry, biomolecules can form polymers.
Examples of polymers include proteins, sugars, nucleic acids, and 3 membranes plus 1 membrane.
Protein is composed of amino acid, sugar is monosaccharide, nucleic acid is composed of nucleotide, ATP
1. The amino acid
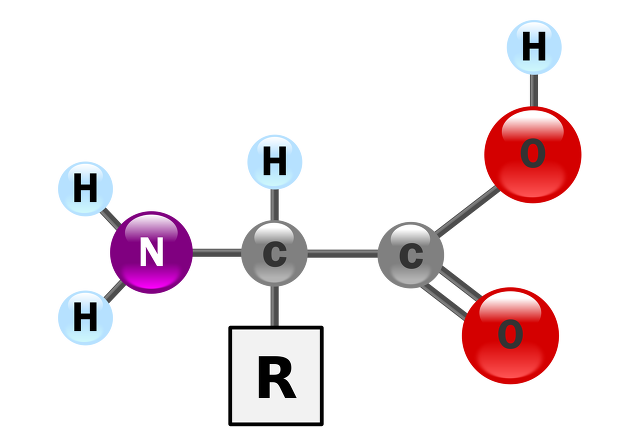
It is based on this structure
2. Carbohydrate (sugar) basically has the formula (CH2O)n

Typically has glucose
3. Nucleic acid is called nucleotide (Nucleotide) and representatively ATP

Adenine is attached as a base, and triphosphate with three ribose (ribose) and phosphorus becomes ATP.
4. Fatty acid is long and has a polarity.

In biochemistry, the unit is necessary because it is viewed from a small molecular perspective.
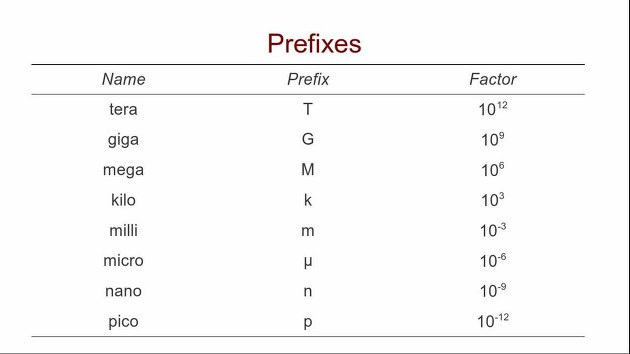
Mega, kilo, milli, micro, nano, pico, femto... You can think of it as ^-3
You can see the text translated here in Korean. : biostudy.tistory.com/5
출처: https://biostudy.tistory.com/190 [do my best, biochemistry:티스토리]


In the periodic table, the most abundant molecules in life are H, C, N, and O,
Next, Na, Mg, P, S, Cl, K, and Ca are the next most abundant.
In addition, B, F, Al, Si, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, As, Se, Br, Mo, Cd, I, W can be considered to play a negative role.
Amine, Alcohol, Thiol, Ether, Aledhyde, Ketone, Carboxylic acid (Carboxylate), Ester, Amide, Imine, Phosphoric acid, Diphosphoric acid should be memorized.
It may be very difficult, but it is essential because it is used for common sense.
wps.prenhall.com/wps/media/objects/3085/3159329/blb2504.html
I think you can refer to it here.
To talk about biomolecules, which are mainly mentioned in biochemistry, biomolecules can form polymers.
Examples of polymers include proteins, sugars, nucleic acids, and 3 membranes plus 1 membrane.
Protein is composed of amino acid, sugar is monosaccharide, nucleic acid is composed of nucleotide, ATP
1. The amino acid

It is based on this structure
2. Carbohydrate (sugar) basically has the formula (CH2O)n

Typically has glucose
3. Nucleic acid is called nucleotide (Nucleotide) and representatively ATP

Adenine is attached as a base, and triphosphate with three ribose (ribose) and phosphorus becomes ATP.
4. Fatty acid is long and has a polarity.

In biochemistry, the unit is necessary because it is viewed from a small molecular perspective.

Mega, kilo, milli, micro, nano, pico, femto... You can think of it as ^-3
You can see the text translated here in Korean. : biostudy.tistory.com/5
출처: https://biostudy.tistory.com/190 [do my best, biochemistry:티스토리]
댓글
댓글 쓰기